The 2024 Summit of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC) was held in Beijing from September 4 to 6, during which Chinese and African leaders renewed friendship, discussed cooperation and discussed the future under the theme of "Jointly Advancing Modernization and Building a high-level China-Africa Community with a shared future". This is another happy reunion of the friendly family of China and Africa following the Beijing Summit in 2006, Johannesburg Summit in 2015 and Beijing Summit in 2018.
In the past few decades, China-Africa cooperation has made great achievements, not only in the fields of economy, agriculture and education, but also in medical and health cooperation. It is foreseeable that during this summit, China and Africa will plan new cooperation measures, including in the field of medicine, and China-Africa medical cooperation will usher in new development opportunities.
China-africa medical cooperation
Fruitful results
Medical and health cooperation is an important part of China-Africa friendly cooperation. Since China sent its first medical team to Algeria in 1963, the cooperation between China and Africa in the field of health has been deepened and expanded and achieved fruitful results.
Trade in medicine is growing steadily
According to the data of the United Nations International Trade Center (ITC), as the mainstream way of China-Africa medical cooperation, bilateral medical trade has maintained a steady growth overall, from $732.1 million in 2014 to $988 million in 2023, with a compound annual growth rate of 3.04%. According to Chinese Customs statistics, from January to June 2024, China-Africa pharmaceutical trade continued to maintain a growth trend, with a year-on-year growth of 8.35%.
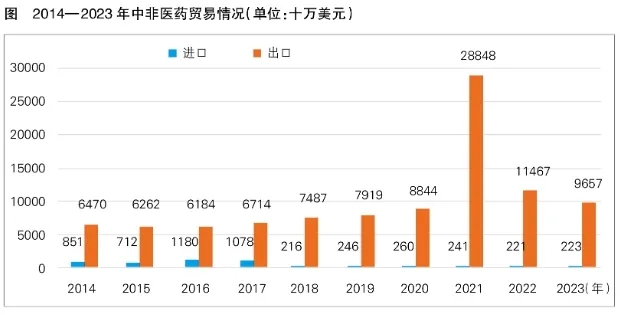
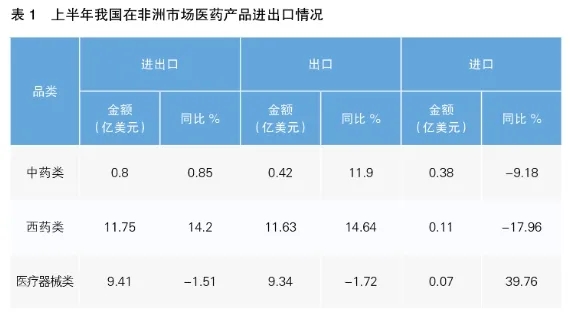
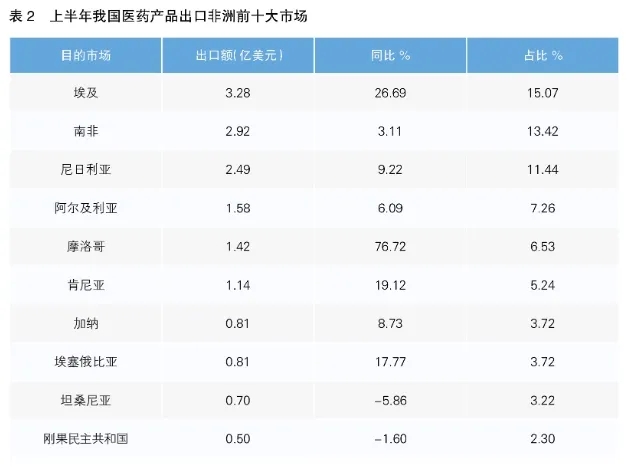
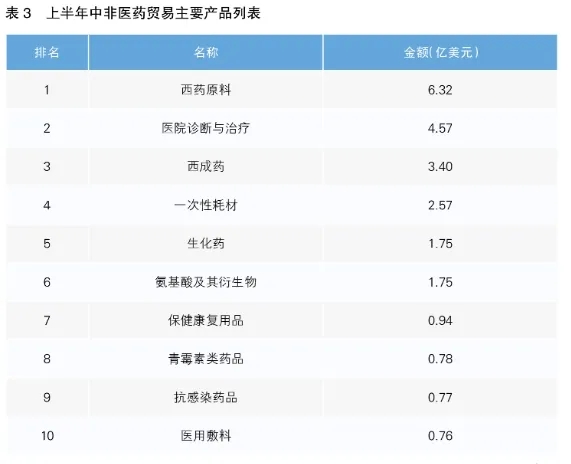
The pace of investment in Africa was accelerated
The earliest investment of Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises in Africa can be traced back to the 1990s of last century. With the implementation of the follow-up policies and measures of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, medical investment and financing cooperation in Africa has gradually become the mainstream development direction of future cooperation.
According to incomplete statistics, Shanghai Pharmaceutical Group has invested in the establishment of production bases in Sudan, Renfu Pharmaceutical in Mali, Fosun Pharmaceutical in Cote d 'Ivoire, and East Sunshine in Algeria, and these enterprises have become representatives of Chinese pharmaceutical enterprises to invest in and cooperate in the production of pharmaceutical preparations and other products in Africa.
At the same time, BGI has invested in factories in Angola, Wambond Group in South Africa, Tianjin Yongkuo in Uganda, and Zhende Medical in Kenya, becoming representatives of medical device product cooperation.
In addition, enterprises and individuals such as China Nonferrous Metals, China Railway Fourth Bureau, Zhongtai Senda, Huali Group have also carried out cooperation in hospital construction in Ethiopia, Angola, Zambia and other countries.
Remarkable achievements have been made in medical assistance cooperation
China has actively carried out medical assistance to Africa, which has played a positive role in improving the medical and health standards of recipient countries and achieved remarkable results.
Medical teams sent to Africa
The year 2023 marks the 60th anniversary of China's dispatch of medical teams to Africa. By 2023, China has sent 24,000 medical teams to Africa, and 45 medical teams are working in 44 African countries to help improve the medical and health standards of the recipient countries and benefit the local people.
Short-term medical assistance to Africa
For example, the hospital ship Peace Ark of the Chinese Navy visited Africa to provide humanitarian medical services. We have carried out many "Bright Action" medical aid services to Africa, and sent light to African cataract patients.
Responding to major public health crises
During the Ebola outbreak in West Africa in 2014, China was the first to offer assistance, sending more than 1,000 public health experts and medical workers to provide medical security and several rounds of emergency assistance to the African people. Since the outbreak of COVID-19 in 2020, the Chinese government has helped African countries fight the epidemic by sending public health experts and medical workers, providing several rounds of supplies such as vaccines, and implementing the G20 initiative to suspend debt repayment for the poorest countries.
Foreign aid training course
Guided by the philosophy that it is better to teach people how to fish than to give them fish, the Chinese government has actively trained local medical and health professionals in Africa, including medical personnel training, the construction of pharmaceutical industrial parks, and the prevention and treatment of major infectious diseases.
Medical infrastructure development
In January 2023, the China-assisted African Center for Disease Control and Prevention Headquarters project (Phase I) was completed, becoming one of the landmark projects of China-Africa medical cooperation. Since 2000, China has helped build more than 130 hospitals and clinics in Africa, improving the public health infrastructure of African countries.
Medical material assistance
China has long provided medical product assistance to African countries to help them upgrade their public health systems and enhance their ability to respond to public health emergencies. Among them, China's compound artemisinin antimalarial drugs have played an important role in helping Africa fight malaria.
Regulatory cooperation is a bright spot
Officially established in November 2021, the African Medicines Agency (AMA) is the second African Union-specific health agency on the continent, after the African Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and is now playing a growing role in coordinating legislation, monitoring coordination, market access authorization, and supporting local pharmaceutical companies to develop and expand markets. China actively supports the work of AMA and has carried out a lot of cooperation in laboratory construction and personnel training. The two China-Africa Medical and Health Development Forums to be held in 2021 and 2023 both focused on China-Africa medical regulatory cooperation, building a new platform for cooperation and exchanges between regulatory departments of the two sides.
China-africa medical cooperation
Many challenges remain
While achieving the above achievements, China-Africa medical cooperation also faces many challenges, which are mainly reflected in the following three aspects.
The business environment of African countries is relatively backward
In the field of public health, Africa has inadequate infrastructure such as hospitals and medical equipment, shortage of medical professionals, and insufficient investment in medical and health care. At the same time, African countries have been deeply troubled by election turmoil, frequent outbreaks of COVID-19, terrorist activities and poverty, and the "four conditions" composed of "election situation, epidemic situation, fear situation and poverty situation" are the main reasons affecting the business environment in Africa. According to the Global Business Environment report released by the World Bank, the soft and hard business environment problems such as power shortage, financing difficulties, and complicated approval procedures have brought many explicit and implicit obstacles to enterprises to carry out medical cooperation in Africa.
Soft supporting facilities closely related to medical cooperation are weak
On the one hand, the degree of regulatory cooperation is insufficient: African countries in the language including Arabic, English, French, Portuguese countries, in the pharmaceutical industry policy, standard setting, regulatory access and product consumption and other aspects are deeply influenced by the former master countries, and each has its own characteristics, coupled with the uneven development of the pharmaceutical industry in various countries, resulting in the overall fragmentation of the African pharmaceutical market, although the African Pharmaceutical Agency has been established. However, the integration of drug regulatory policies is still in its infancy, which has brought many difficulties to pharmaceutical investment access, product certification and product sales.
On the other hand, the supporting fund is insufficient: The pharmaceutical industry is a high-tech and high-capital investment industry. African countries have limited financial resources and are deeply troubled by debt. Western countries represented by the United States attach more conditions to their funds, some international institutions pay lip service to their funds, and Africa's local financing channels are narrow. The shortage of funds and financing difficulties exist in different degrees. According to the survey, many pharmaceutical companies listed financing problems along with security issues, political risks, exchange rate fluctuations and fierce competition as the top five obstacles to investment in Africa.
Facing fierce international competition
First, in terms of cooperation mechanisms, the medical and health cooperation measures planned by FOCAC have become the main driving force for China-Africa medical cooperation, which also faces a lot of competition. The United States, the European Union, Russia, Japan, India, South Korea and other countries and regions have established "summit" mechanisms with Africa, all involving medical cooperation, and "benchmarking" China in policy formulation, capital investment, project implementation, and personnel training.
Second, in terms of market competition pattern, drugs in Europe and the United States not only have patent technology advantages, but also enjoy registration, certification and access convenience, and the African high-tech high-end drug market is basically monopolized by products in Europe and the United States.
Indian pharmaceutical companies mainly enter the African market through non-governmental organizations and public market bidding. Indian companies such as Sipra, Ranbaxy, Serum Institute of India, and Dr. Reddy have performed well in the African market of English-speaking countries, and have advantages such as relatively complete supply and marketing networks, coupled with their leading position in the field of generic drugs. The middle - and low-end pharmaceutical market in Africa is largely occupied by Indian products.
China-africa medical cooperation
To achieve new development requires precise measures
There is huge potential for China-Africa medical cooperation, and there is a long way to go. It requires the joint efforts of all parties to address issues such as policy coordination, basic supporting facilities, standard access, personnel exchanges and project docking, and more precise support policies need to be introduced. The author puts forward relevant suggestions as follows
Set up medical products supply for China and Africa
Guarantee warehouse and sales wholesale center
According to UNAIDS, 97% of medicines in Africa come from outside the continent and only 3% are produced locally.
African countries already have a high incidence of diseases, and there is a greater demand for Chinese pharmaceutical products with high quality and good prices. In particular, after the outbreak of COVID-19, when African countries needed to purchase anti-epidemic supplies, China quickly extended a helping hand to Africa, providing a large number of anti-epidemic supplies to the African Union and African countries, and sending medical teams to help African countries in epidemic prevention and treatment.
To this end, it may be considered to set up medical product supply guarantee warehouses and wholesale sales centers in several regions of the African continent to facilitate African countries to buy Chinese medical products and avoid purchasing difficulties and quality concerns caused by information asymmetry.
A China-Africa medical cooperation fund will be established
Medical cooperation belongs to the field of high technology, high capital and high threshold, and is particularly sensitive to the need for funds. To this end, the China-Africa medical Cooperation Fund may be set up with reference to the China-Africa Production Capacity Cooperation Fund and other models to provide support in investment risk assessment, market development, project feasibility studies and policy coordination, so as to reduce the financial pressure on enterprises and jointly share cooperation risks.
We will hold the China-Africa Forum on Medical Regulation Cooperation
The African Pharmaceutical Administration has been established, and it is proposed to support the holding of the China-Africa Pharmaceutical Regulatory Cooperation Forum under the framework of the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, so as to create a higher level platform for China-Africa pharmaceutical regulatory cooperation and exchanges, and also create regulatory access convenience for China-Africa pharmaceutical industry cooperation.
We will support Chinese enterprises in going to Africa
Localization of medical products
Africa's indigenous pharmaceutical industry is underdeveloped. It is understood that African countries welcome Chinese pharmaceutical companies to cooperate in local drug production. This demand has increasingly become the "largest common denominator" of China-Africa medical cooperation, and it is recommended to increase efforts and investment in this cooperation.
An exhibition on China-Africa medical and health products will be held
From the current situation of China-Africa pharmaceutical trade cooperation, it is still dominated by Chinese exports. In order to facilitate the African demand side to better purchase relevant products and negotiate relevant cooperation, it is suggested that the China-Africa medical and health products exhibition be held in rotation in relevant African countries, so as to provide an effective platform for better docking and cooperation between the supply and demand side.
Innovative ways of providing medical assistance to Africa
We will further help African countries improve their public health systems and enhance their capacity to guarantee public medical services. For example, we should carry out comprehensive cooperation in anti-malaria and anti-AIDS prevention and control, and realize the transformation from simple material assistance to comprehensive prevention and control. In addition, we can also actively carry out trilateral cooperation to organically combine China's "hard power" in products and technology with the "soft power" of relevant international institutions and countries in the formulation of project plans, resource allocation and project implementation in Africa, so as to amplify the influence and effect of China's cooperation projects in Africa.
|
Last:Reproduced: Reprint: high-quality development of service trade
Next:Reproduced: State Medical Insurance Bureau |
Return |